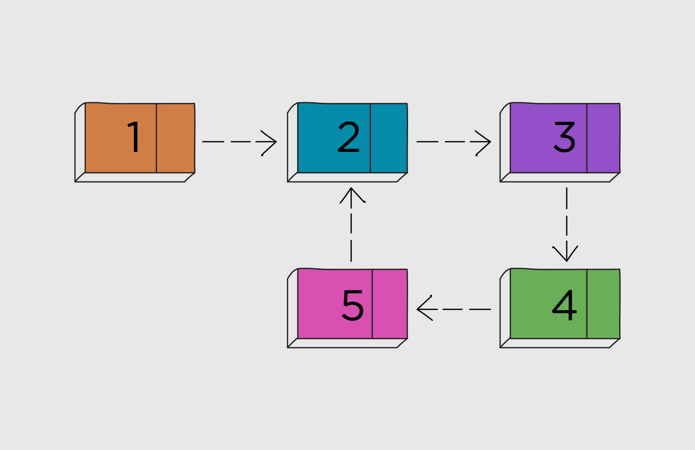
What is a loop in a linked list
A very common operation in a linked list is to traverse throughout the LinkedList. But when no null value is reached as traversing throughout the linked list, we call this as loops in a linked list. So to detect whether a LinkedList has a loop or not, we can use Floyd’s Cycle-Finding Algorithm also known as a slow-fast pointer or hear tortoise algorithm.
We are implementing Floyd’s Cycle-Finding Algorithm to find loops in a linked list
Linked List
Node & Linked list struct
type Node struct {
data interface{}
next *Node
}
type LinkedList struct {
head *Node
}
Push to a Linked List
func (ll *LinkedList) Push(data interface{}) {
list := &Node{
data: data,
}
list.next = ll.head
if ll.head != nil {
ll.head = list
}
ll.head = list
l := ll.head
for l.next != nil {
l = l.next
}
}
Display the Linked list
func (ll *LinkedList) Display() {
list := ll.head
for list != nil {
fmt.Printf("%+v -> ", list.data)
list = list.next
}
fmt.Println()
}
Detect loops in LinkedList using Floyd’s Cycle-Finding Algorithm
func (ll *LinkedList) DetectLoop() bool {
slowPtr := ll.head
fastPtr := ll.head
for slowPtr != nil && fastPtr != nil && fastPtr.next != nil {
slowPtr = slowPtr.next
fastPtr = fastPtr.next.next
if slowPtr == fastPtr {
return true
}
}
return false
}
If you like, you can read the same article on my Personal Blog
Main function
func main() {
link := LinkedList{}
link.Push(1)
link.Push(2)
link.Push(3)
link.Push(4)
link.Push(5)
// creating a loop in the above linked list
link.head.next.next.next.next.next = link.head // comment this then for no loop
if link.DetectLoop() {
fmt.Println("found loop")
} else {
fmt.Println("no loop")
}
}
// output
found loop