Full–text search refers to the advanced functionality in SQL Server that supports full–text queries against character-based data. These types of queries can include words and phrases as well as multiple forms of a word or phrase. It enables us to search value from multiple fields together and show the result as per the matching rank. Except for the express edition of SQL Server, all other editions have this option.
We can write full-text queries by using the predicates CONTAINS and FREETEXT and the rowset-valued functions CONTAINSTABLE and FREETEXTTABLE with a SELECT statement.
CONTAINS/CONTAINSTABLE:
Match single words and phrases with precise or fuzzy (less precise) matching.
FREETEXT/FREETEXTTABLE:
Match the meaning, but not the exact wording, of specified words, phrases, or sentences. Matches are generated if any term or form of any term is found in the full-text index of a specified column.
Here I will try to show an example of FREETEXT and FREETEXTTABLE in a simple way step by step—
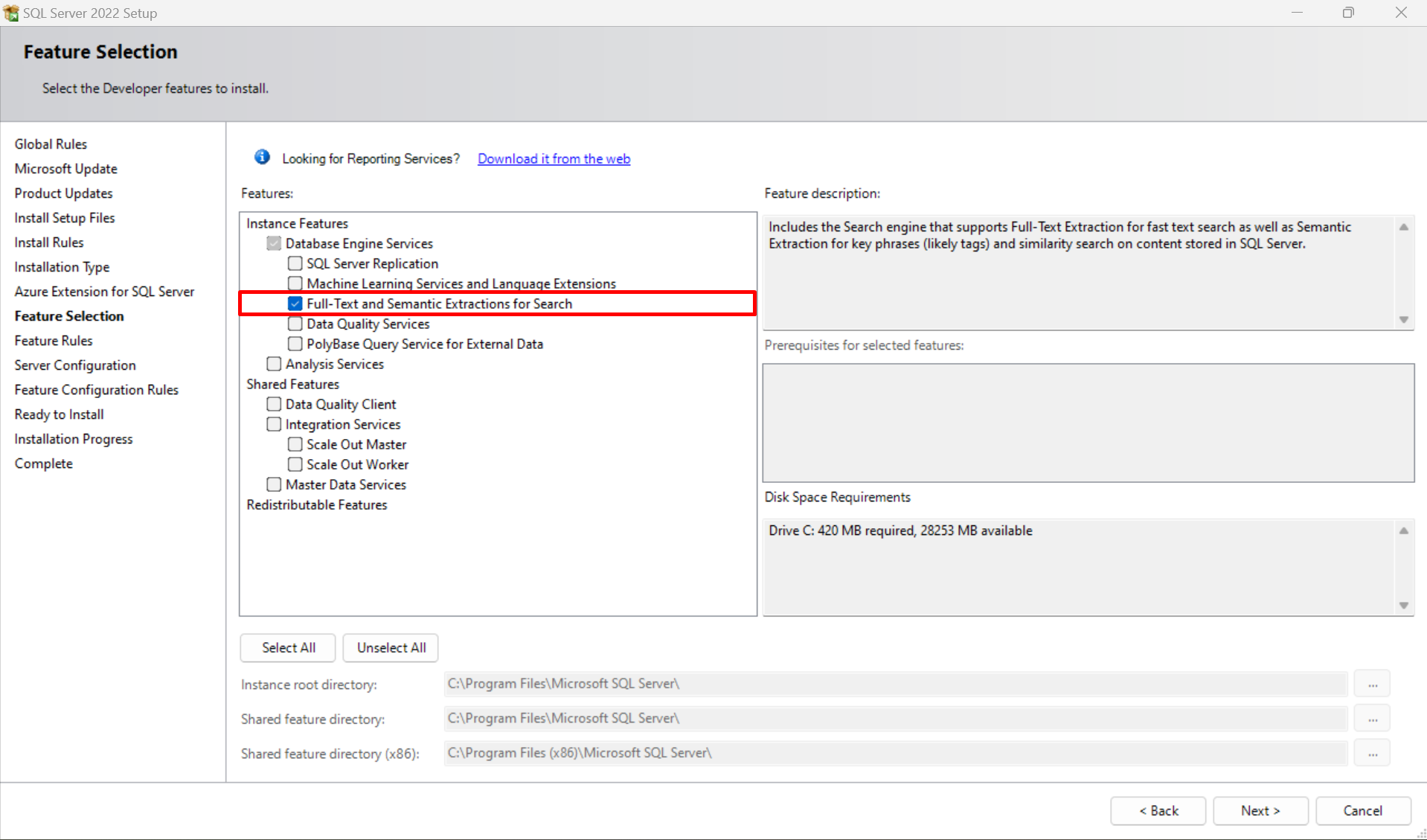
2) Create Full-Text catalog—
CREATE FULLTEXT CATALOG SearchCatalog AS DEFAULT;
GO
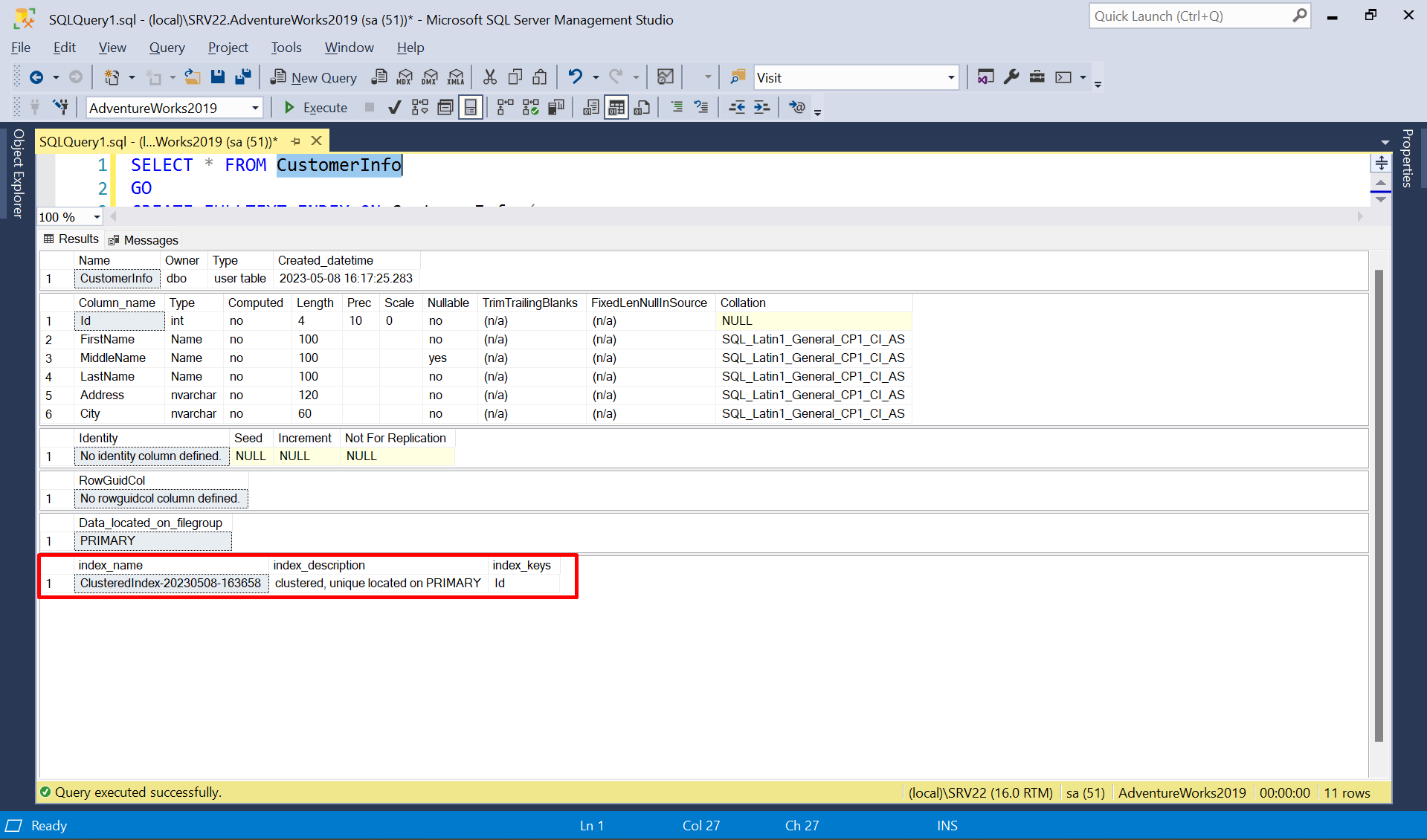
3) Now we have to create Full-Text INDEX
to table on which we want to enable Full-Text search option. To enable Full-Text INDEX on desired table need to have a Clustered INDEX. To Check it has clustered index or not select table name and press ALT + F1. If there is no clustered index found then create one clustered index on the Id column.
CREATE UNIQUE CLUSTERED INDEX [PK_CustomerInfo] ON [dbo].[CustomerInfo]([Id])
GO
Now create Full-Text INDEX—
CREATE FULLTEXT INDEX ON CustomerInfo (
FirstName,
MiddleName,
LastName,
[Address],
City
) KEY INDEX PK_CustomerInfo
GO
To get a tailored application hire Developers from us
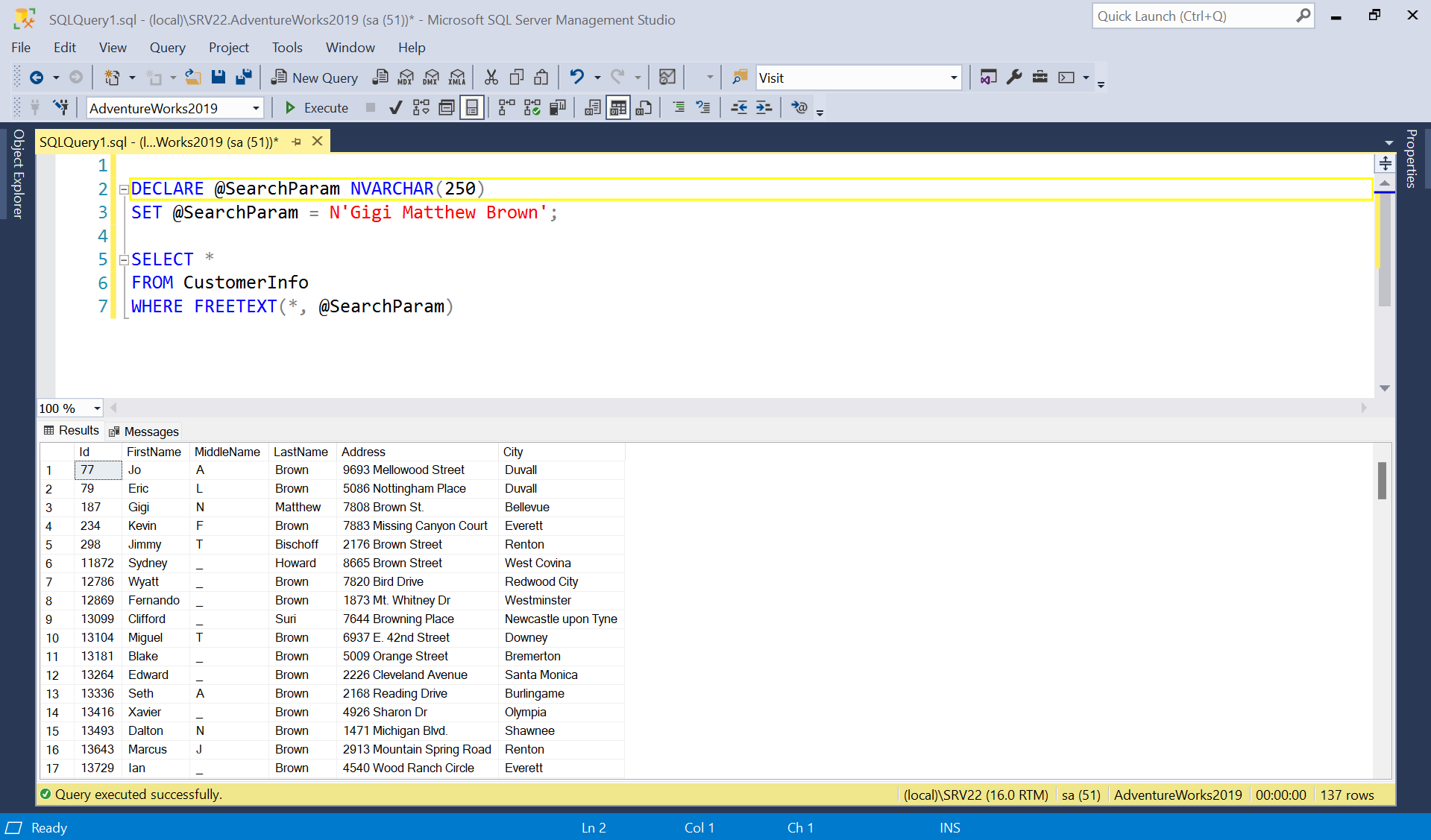
5) We can enhance the query to show the result with match rank/score—
DECLARE @SearchParam NVARCHAR(250)
SET @SearchParam = N'Gigi Matthew Brown';
SELECT
ftt.RANK,p.*
FROM CustomerInfo p
INNER JOIN FREETEXTTABLE(CustomerInfo, *, @SearchParam) as ftt ON ftt.[KEY] = p.Id
ORDER BY ftt.RANK DESC
GO
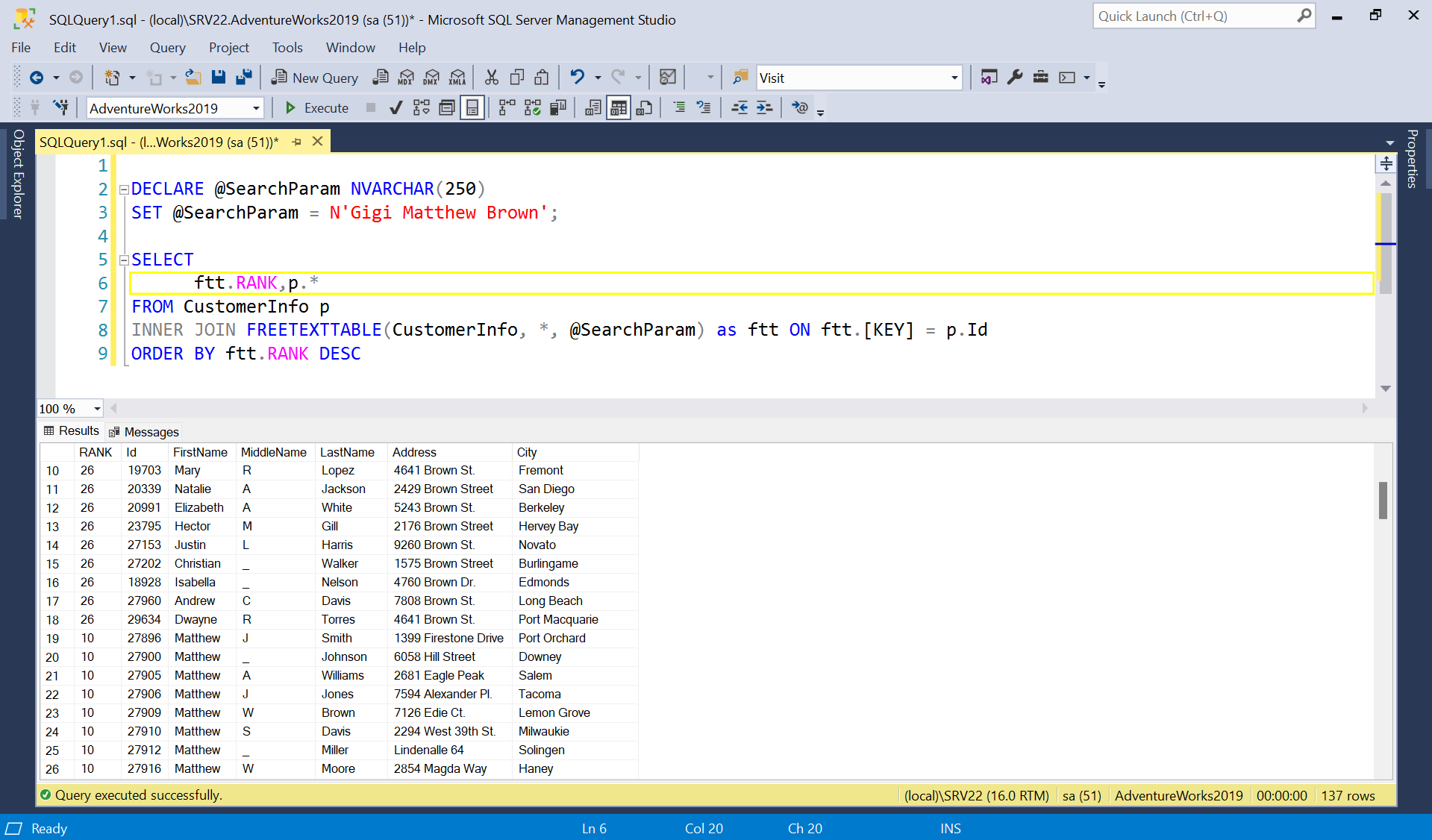
RANK that contains ordinal values from 0 through 1000 (rank values). These values are used to rank the rows returned according to how well they match the selection criteria. The rank values indicate only a relative order of relevance of the rows in the result set. The actual values are unimportant and typically differ each time the query is run.
I hope this will help a bit to enable better search functionality. In addition to this we can create SQL View with SCHEMABINDING and Unique Clustered index to enable Full-Text search option on a SQL View.
Next, we will create an indexed view with Full-Text search option.